The human knee is a complex and intricate joint with varying structures that include bones, ligaments, tendons, muscles, and other types of connective tissues. Each of your knees plays a critical role in your mobility as well as in helping to support your body weight.
Your knees are always at work from the moment you want up in the morning to the point where you go to bed at night. They can even play a role in sleep quality as well as helping you roll over or change position comfortably while sleeping. So, it is not an overstatement to say that each of your knees plays a critical role in your overall quality of life.
Though it is an unfortunate truth that as we age all the activities and stresses we put our knees through can start to build up in wear and tear on our knee joints. As time goes on, this can lead to knee problems that cause pain, it can also increase your risk of developing arthritis as well as other potentially serious knee problems.
With most of these conditions, acute or chronic knee pain is one of the first signs of a problem. While you might be able to put it out of your mind and ignore the pain in one or both of your knees, you could be doing so at your own peril. Having your knees examined by an experienced and licensed medical professional who specializes in orthopedic injuries is a wise first step toward managing, treating, reducing, or preventing further knee problems in the future.
The Effects Of Chronic Knee Pain
It is a salient truth that chronic knee pain can take a heavy toll on your daily quality of life. The persistent discomfort can easily keep you from some of your favorite activities. Not to mention its ability to sap you of your productivity, as well as diminish your overall quality of life.
For some people struggling to deal with chronic knee pain a special treatment known as a Genicular Nerve Block. This can be a standalone treatment or part of a larger treatment strategy to address a variety of underlying chronic knee pain problems.
Osteoarthritis in one or both of the knees is one of the most common underlying causes of chronic knee pain. It is typically the product of normal wear-and-tear that builds up as you age. The gradual weakening and degradation of the protective cartilage surrounding your knee are often degenerative. This essentially means that without treatment, the osteoarthritis pain will simply continue to grow worse as time goes on.
What Is A Genicular Nerve Block?
A genicular nerve block can be used to both diagnose as well as treat chronic knee pain. It usually comes in the form of a special type of injection that contains both a local anesthetic as well as a corticosteroid. This serves to both numb the distressed tissues, as well as help to reduce the inflammation in the surrounding tissues.
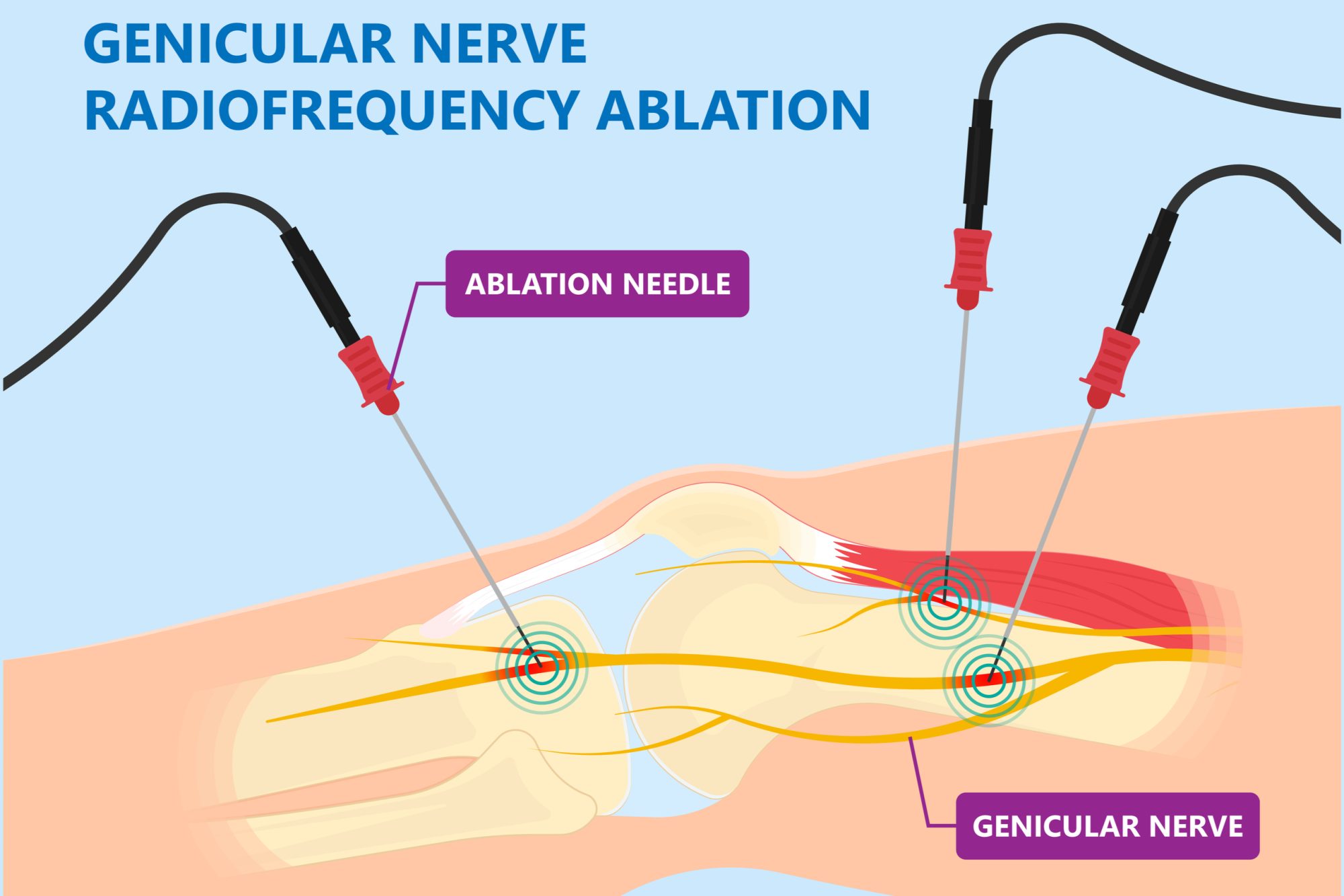
A physician will administer the injection into one or more genicular nerves in the knee. Of them, there tend to be three main articular branches of genicular nerves that are ideal locations for the injection. Your physician will assess whether it is best to inject in one, two, or all three locations.
They are known as the superior medial, superior lateral, and anterior medial. The genicular nerve block injection essentially bathes the related genicular nerve branch with the specially blended medication. This in turn interrupts the pain signals before they can be sent to your brain.
How Is A Genicular Nerve Block Performed?
A Genicular-Nerve Block procedure is typically administered on an outpatient basis. The injection itself should only take roughly 15 to 20 minutes.
During the procedure, the physician will cleanse and numb the injection site and many of the tissues surrounding the knee. At that point, the injection will be administered under fluoroscopic guidance. This is a type of imaging technology that helps the doctor to accurately place the needle tip using X-ray guidance and a high-contrast dye. Once it starts to take effect your physician might observe you for an additional 15 to 20 minutes to ensure it is fully taking effect. At that point, can leave after your procedure.
It’s worth bearing in mind that some individuals choose to receive IV sedation to help them remain comfortable throughout the injection process. Though if you do choose this option, you will need to make arrangements for someone to drive you home. Some people feel side effects after sedation which typically include dizziness, lightheadedness, and nausea.
How Long Do The Effects Of A Genicular Nerve Block Last?
Most patients who receive a genicular nerve block will note feeling almost immediate short-term relief. For most this lasts a full 8 to 24 hours. These temporary effects are intentional as many times a genicular nerve block is used to test the effectiveness of more intensive treatments. Especially in a diagnostic process known as a genicular rhizotomy, or a radiofrequency ablation (RFA).
In this way, a diagnostic genicular nerve block (GNB) is a diagnostic procedure that is usually combined with a local anesthetic to help eliminate discomfort before making decisions regarding an RF ablation. This is a minimally invasive procedure that can provide pain relief for six months to perhaps a year.
What Conditions Can A Genicular Nerve Block Be Used To Treat?
The good news is that a genicular nerve block can be used to help diagnose and provide relief from a wide range of knee pain conditions. This includes things like:
- Knee arthritis
- Severe osteoarthritis affecting the knee
- Failed total or partial knee replacement surgery
- Degenerative joint disease in the knee
- Chronic knee pain for conditions where there isn’t a viable surgical option
If you’ve been struggling to deal with chronic knee pain and it is hampering your mobility or your overall quality of life, it’s important to understand that you have options. Scheduling a diagnostic consultation with an orthopedic specialist represents a first step toward finding the most effective treatment option for your chronic knee pain. This might include using a genicular nerve block injection as part of a diagnostic process or overarching treatment strategy.